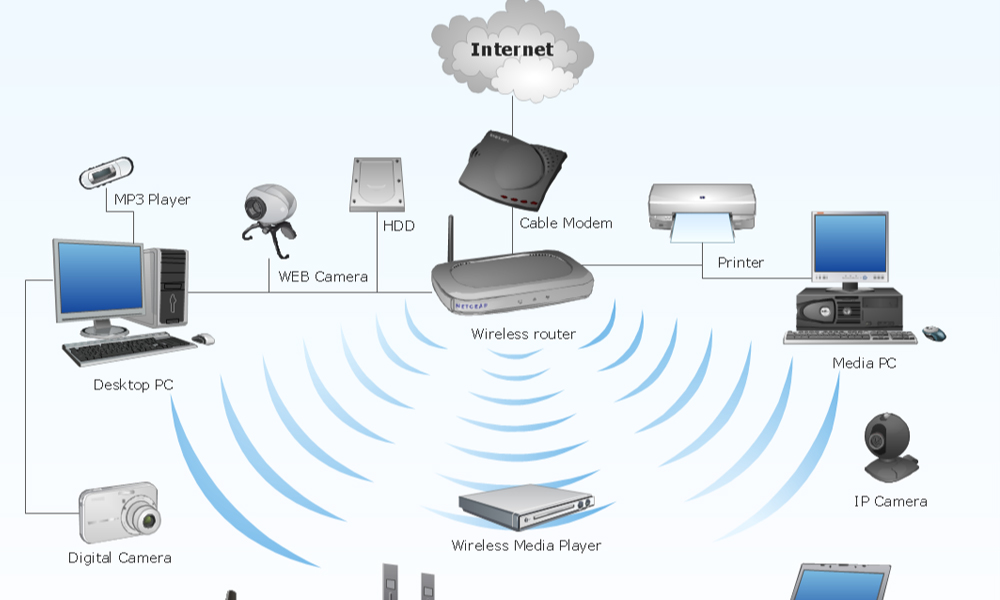
LAN (Local Area Network)
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a network of computers and devices that are interconnected within a limited geographical area, such as a home, office, or building. It allows devices to share resources, data, and applications, and is typically connected using physical cables (like Ethernet) but can also include wireless devices.
Key Features of LAN:
- Limited Scope: Usually confined to a small geographic area like a single building or campus.
- Speed: Typically high-speed, ranging from 100 Mbps (Ethernet) to 10 Gbps and beyond.
- Reliability: Generally stable and less prone to interference, especially when using wired connections.
- Hardware: LANs consist of routers, switches, hubs, access points, and computers or other connected devices.
- Connectivity: Devices within a LAN communicate through dedicated protocols such as Ethernet and Wi-Fi.
- Control: Organizations or users can have control over the network’s infrastructure and security.
Wireless Network (Wi-Fi)
A wireless network uses radio waves to transmit data between devices without the need for physical cabling. Most wireless networks are based on Wi-Fi (Wireless Fidelity) standards, making it easy for devices such as smartphones, laptops, tablets, and IoT devices to connect without wires.
Key Features of Wireless Networks:
- Flexibility: Devices can connect to the network from various locations within a specified range.
- Standard: Wi-Fi networks follow IEEE 802.11 standards, with different versions like 802.11a, 802.11b/g/n, and 802.11ac offering varied speeds and range.
- Speed and Range: Speed varies from 11 Mbps (older standards) to several gigabits per second (e.g., Wi-Fi 6, 802.11ax). Range typically extends between 100 to 300 feet indoors.
- Interference: Wireless signals are more prone to interference from physical barriers (walls, floors) and other devices (e.g., microwaves, Bluetooth devices).
- Convenience: Allows easy mobility within coverage area without the need for cables.
- Security: Wireless networks must implement security protocols (e.g., WPA3, WPA2) to prevent unauthorized access.
Key Differences Between LAN and Wireless Network:
| Feature | LAN (Wired) | Wireless Network (Wi-Fi) |
| Medium | Cables (Ethernet, Fiber, etc.) | Radio waves (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth) |
| Range | Limited to a building or campus | Varies, generally within 100–300 feet (indoors) |
| Speed | Generally faster (up to 10Gbps) | Varies, but slower than wired (up to several Gbps in newer standards) |
| Stability | More stable (less prone to interference) | Can experience interference (e.g., from walls, other devices) |
| Mobility | Fixed devices (stationary) | Allows device mobility within coverage area |
| Installation | Requires running cables | Easier to deploy, no cabling needed |